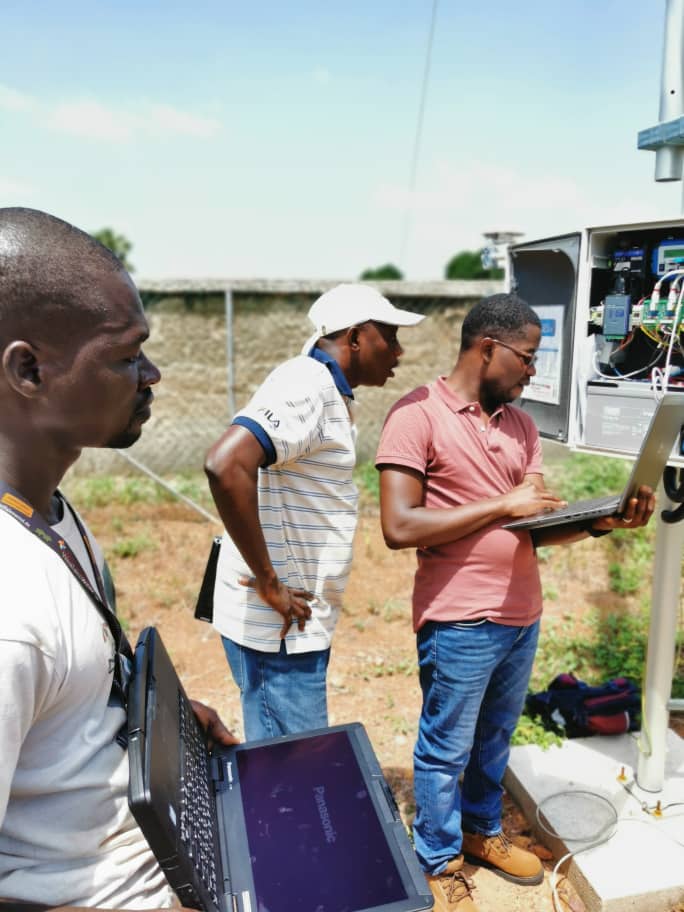
In this interview, Paul David Bohn from Cologne University of Applied Sciences talks about his role in the EnerSHelF project. He continues the work of Silvan Rummeny on an advisor and planning tool for Photovoltaic-diesel-hybrid systems.
In autumn 2021, you took over the role of Silvan Rummeny, who was working in work package 3.3. Can you tell us what his – and now your – work entails?
The main subject of work package 3.3. is the development of an advisor and planning tool for micro grids. The acronym for this tool is Micro Grid User Energy Planning TooL (MiGUEL). MiGUEL is used to design, simulate and evaluate Photovoltaic (PV)-diesel-hybrid systems for Ghanaian health facilities. The goal is to provide users with suitable solutions on how to design a cost-effective micro grid, contributing to fulfil the sustainable development goals and affiliated roadmaps. The target groups are project developers, engineering companies, and private as well as public grid operators who want to implement micro or mini grids. Silvan Rummeny started designing MiGUEL and I took over the development since he left EnerSHelF.
Continue reading Continuing the development of the planning tool for micro grids